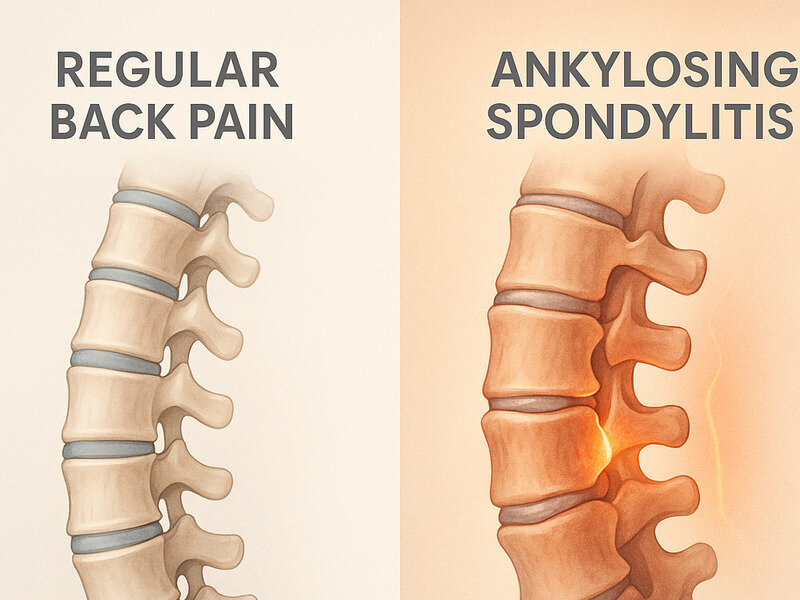
Back pain is a common ailment affecting millions worldwide, often resulting from poor posture, injury, or lifestyle habits. However, not all back pain is created equal. Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease that can cause severe back pain and is often mistaken for regular back pain. Understanding the differences between these two conditions is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.
Overview of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis is a form of arthritis primarily affecting the spine, although other joints can also be involved. It leads to inflammation of the spinal joints, which can cause chronic pain and discomfort. Over time, AS can result in the fusion of vertebrae, leading to a loss of flexibility and a hunched posture.
According to the Spondylitis Association of America, AS affects approximately 0.1% to 1.4% of the population, with men being more commonly affected than women. The onset typically occurs in late adolescence or early adulthood.
Characteristics of Regular Back Pain
Regular back pain, often referred to as mechanical back pain, is usually caused by muscle strain, ligam...
Premium preview
Premium members unlock the full article—complete step-by-step routines, deeper coaching notes, and exclusive frameworks.


